Observation 6.8.1.
The name of the order is based on where the root is visited; in preorder, we visit it first. For inorder, we visit it in the middle, and for postorder, we visit it last.
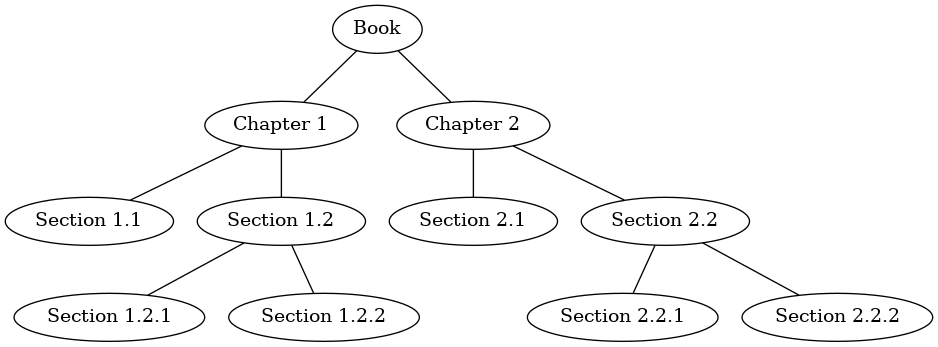
preorder on the left child, in this case Chapter1. We again recursively call preorder on the left child to get to Section 1.1. Since Section 1.1 has no children, we do not make any additional recursive calls. When we are finished with Section 1.1, we move up the tree to Chapter 1. At this point we still need to visit the right subtree of Chapter 1, which is Section 1.2. As before we visit the left subtree, which brings us to Section 1.2.1, then we visit the node for Section 1.2.2. With Section 1.2 finished, we return to Chapter 1. Then we return to the Book node and follow the same procedure for Chapter 2.BinaryTree class, or should it be a method of the tree data structure itself? Listing 6.8.3 shows a version of the preorder traversal written as a static method that takes a binary tree as a parameter. The static method is particularly elegant because our base case is simply to check if the tree exists. If the tree parameter is null, then the function returns without taking any action.public static void preorder(BinaryTree<String> tree) {
if (tree != null) {
System.out.println(tree.getRootValue());
preorder(tree.getLeftChild());
preorder(tree.getRightChild());
}
}
preorder as a method of the BinaryTree class. The code for implementing preorder as an internal method is shown in Listing 6.8.4. Notice what happens when we move the code from external to internal. In general, we just replace tree with this. Also, because this method is part of BinaryTree, it can directly access the fields. However, we also need to modify the base case. The internal method must check for the existence of the left and the right children before making the recursive call to preorder.public void preorder() {
System.out.println(this.key);
if (this.leftChild != null) {
this.leftChild.preorder();
}
if (this.rightChild != null) {
this.rightChild.preorder();
}
}
preorder is best? The answer is that implementing preorder as an external method is probably better in this case. The reason is that you very rarely want to just traverse the tree and print its values. In most cases, you will want to accomplish something else while using one of the basic traversal patterns. In fact, we will see in the next example that the postorder traversal pattern follows very closely with the code we wrote earlier to evaluate a parse tree. Therefore, we will write the rest of the traversals as external methods.postorder traversal, shown in Listing 6.8.5, is nearly identical to preorder except that we move the call to print to the end of the function.public static void postorder(BinaryTree<String> tree) {
if (tree != null) {
postorder(tree.getLeftChild());
postorder(tree.getRightChild());
System.out.println(tree.getKeyValue());
}
}
public static Double postorderEvaluate(BinaryTree>String> tree) {
Double leftValue = null;
Double rightValue = null;
Double result;
if (tree != null) {
leftValue = postorderEvaluate(tree.getLeftChild());
rightValue = postorderEvaluate(tree.getRightChild());
if (leftValue != null && rightValue != null) {
String operator = tree.getRootValue();
if (operator.equals("+")) {
result = leftValue + rightValue;
} else if (operator.equals("-")) {
result = leftValue - rightValue;
} else if (operator.equals("*")) {
result = leftValue * rightValue;
} else {
result = leftValue / rightValue;
}
return Double.doubleValu(result);
}
return Double.parseDouble(tree.getRootValue());
} else {
return null;
}
}
System.out.println call with respect to the two recursive function calls.public static void inorder(BinaryTree<String> tree) {
if (tree != null) {
inorder(tree.leftChild);
System.out.println(tree.key);
inorder(tree.rightChild);
}
}
public static String expressionToString(BinaryTree<String> tree) {
String result = "";
if (tree != null) {
result = result + "(" + expressionToString(tree.leftChild);
result = result + tree.key;
result = result + expressionToString(tree.rightChild) + ")";
}
return result;
}
expressionToString method as we have implemented it puts parentheses around each number. While not incorrect, the parentheses are clearly not needed. In the exercises at the end of this chapter you are asked to modify the expressionToString function to remove this set of parentheses.