3.2.8.1. Fill-In Scope.
Solution.
A parameter variable has local scope.
| accessor method | loop structure | repetition structure |
| class scope | method overloading | scope |
| formal parameter | method signature | selection |
| if statement | mutator method | side effect |
| if/else statement | multiway selection | while statement |
| inherit | override | while structure |
| local scope | polymorphism |
void methods, a method invocation or method call is an expression which has a value of a certain type. For example, nim.getSticks() returns a int value.private. The class’s public methods make up its interface.while statement is used for coding loop structures that repeatedly execute a block of code while a boolean condition is satisfied.setName() method. Of course, there are many other appropriate names for the variables and parameters and other initial assignments.private String nameOne = "Player One";
private String nameTwo = "Player Two";
public void setNames(String name1, String name2)
{ nameOne = name1;
nameTwo = name2;
}
game1 is: game1.setNames("Xena","Yogi");
public OneRowNim(int sticks)
{
nSticks = sticks;
player = 2;
}
public OneRowNim(int sticks, int initPlayer)
{
nSticks = sticks;
player = initPlayer;
}
OneRowNimClass
1
20
false
public int getMoves()
{
return nMoves;
}
public boolean playerOneIsNext()
{
return (player == 1);
}
getStatus() method: 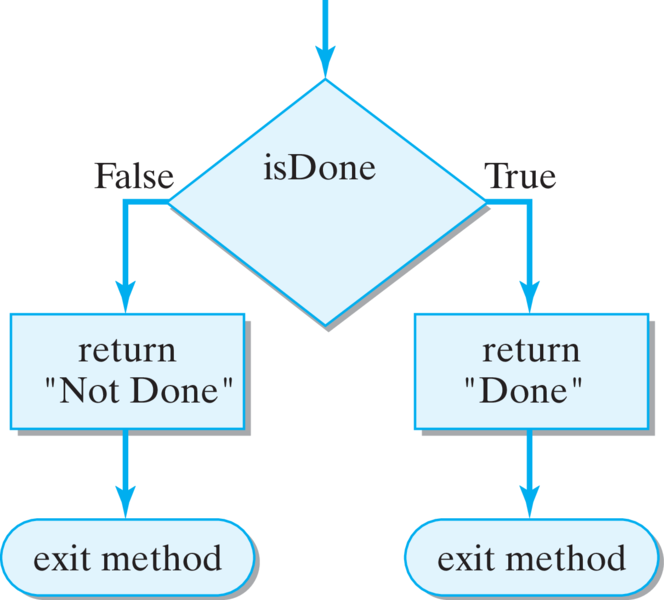
if (isHeavy == true)
System.out.println("Heavy") ;
else ; // Error (remove this semicolon)
System.out.println("Light");
if (isLong == true)
System.out.println("Long")
else // Error (end line above with semicolon)
System.out.println("Short");
public String getPlayerName()
{ if (player == 1)
return "Ann";
else if (player == 2)
return "Bill";
else if (player == 3)
return "Cal";
else
return "Error";
}
public int sumCubes(int min, int max)
{
int num = min;
int sum = 0;
while (num <= max)
{ // While num <= max
sum = sum + num*num*num; // Add cube of num to sum
num = num + 1; // Add 1 to num
} //while
return sum; // Return the sum
}