Section 11.13 Worked Example: Arrays - Minimum Value
Subgoals for Evaluating Arrays.
- Set up array from 0 to size-1
- Evaluate data type of statements against array
-
Trace statements, updating slots as you go
- Remember assignment subgoals
Subsection 11.13.1
You can watch this video or read through the content below it.
Problem: Assume that the integer array
alpha has been properly declared and is full of data values. Evaluate these statements and determine the value of min. If any error occurs, give the reason.int min = alpha[0];
for (int i = 1; i < alpha.length; i++) {
if (alpha[i] < min)
min = alpha[i];
}
Subsection 11.13.2 SG1: Set up array from 0 to size-1
- alpha is an array of ints and has values, but we don’t know what those values are
- however, we can still diagram a representation of this array
- notice that the largest index is size - 1
Subsection 11.13.3 SG2: Evaluate data type of statements against array
The first statement,
int min = alpha[0], is valid because alpha stores integers, and 0 is a valid index. You can assign an int value to an int variable such as min.for (int i = 1; i < alpha.length; i++) {
if (alpha[i] < min)
min = alpha[i];
}
- This loop has index i go from 0 to size - 1 (<length) by increments of 1.
- Then the value at alpha[i] is compared to min. If the value at alpha[i] is less than min, then alpha[i] is copied into min.
- All indexes into the array are valid, and all assignments are valid.
Subsection 11.13.4 SG3: Trace statements, updating slots as you go
Let us trace with a sample array.
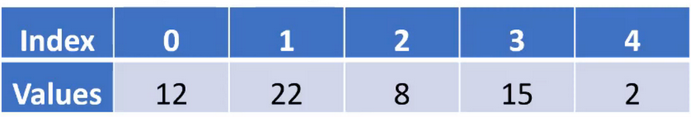
The first line of the code sample initializes
min to copy the value from alpha[0], which in our sample is 12, and then a for-loop is used to traverse the array. The chart below uses one line to represent the memory and calculations during each iteration of the loop, starting when i has a value of zero.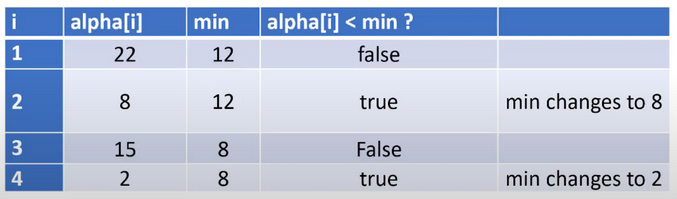
We can see that each time a smaller value is located in the array, that value is stored in
min.The more general answer to the original question is: “
min contains the smallest value found in the array alpha.”Subsection 11.13.5 Practice Pages
You have attempted of activities on this page.
