Section 11.17 Worked Example: Arrays - Find Value
Subgoals for Evaluating Arrays.
- Set up array from 0 to size-1
- Evaluate data type of statements against array
-
Trace statements, updating slots as you go
- Remember assignment subgoals
Subsection 11.17.1
You can watch this video or read through the content below it.
Problem: Assume that the integer array
alpha has been properly declared and is full of data values, and that the variable target is an int with a value in it. Evaluate these statements and determine the value of loc. If any error occurs, give the reason.int loc = -1;
boolean found = false;
for (int i = 0; i < alpha.length && !found; i++) {
if (alpha[i] == target) {
loc = i; found = true;
}
}
Subsection 11.17.2 SG1: Set up array from 0 to size-1
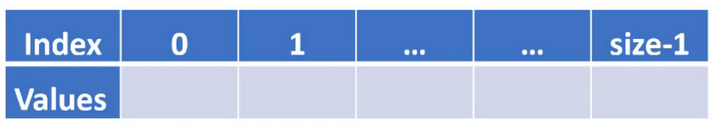
- alpha is an array of ints and has values, but we don’t know what those values are
- however, we can still diagram a representation of this array
- notice that the largest index is size - 1
Subsection 11.17.3 SG2: Evaluate data type of statements against array
References to the array are in the loop and selection statements:
for (int i = 0; i < alpha.length && !found; i++) {
if (alpha[i] == target) {
loc = i; found = true;
}
}
- This loop has index i go from 0 to size - 1 (<length) by increments of 1.
- Then the value at alpha[i] is compared to the int value of target.
- If the value at alpha[i] is equal to target, then the value i is copied into loc.
- All indexes into the array are valid, and all assignments are valid.
Subsection 11.17.4 SG3: Trace statements, updating slots as you go
Let us trace with a sample array and assume the value of
target is 15.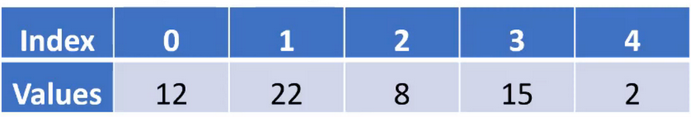
The first statement,
int loc = -1; gives loc a value that is not a valid index for any array.Then a for-loop is used to traverse the array and compare each element to
target. The chart below uses one line to represent the memory and comparisons during each iteration of the loop, starting when i has a value of zero.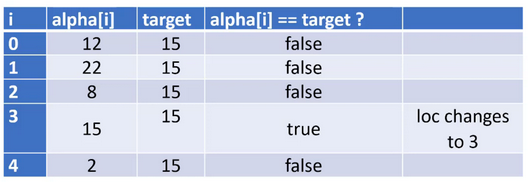
When we find the target value in the array, we store the index (location) of where it is in the array.
Some questions to consider:
- What would happen if the
targetvalue is not in the array? Then the selection statement is never true, andlocis never changed from its initial value of -1. - Why is -1 a good initial value for
loc? It is not a valid index for any array. You or another programmer using this algorithm could check the value oflocto make a decision (selection!) for how the program will behave when thetargetvalue is found or not found at a valid array index. - What would happen if there were 2 occurrences of the target value in the array? The loop does not end when the
targetvalue is found, so additional occurences would overwrite the value oflocwith the last occurence.
The more general answer to the original question is: “
loc contains the index of the last occurrence of target in the array alpha or -1 if target is not in the array.”Subsection 11.17.5 Practice Pages
You have attempted of activities on this page.
