7.3. Traversing ArrayLists with Loops¶
ArrayLists can be traversed with while loops and both regular and
enhanced for loops much the same way we use those constructs to loop over an
array.
7.3.1. Enhanced For Each Loop¶
You can use a enhanced for loop to traverse all of the items in an
ArrayList, just like you do with an array when you only care about the
values in the list and not their indices. An example is shown in the main
method below.
Note however that you can’t use the enhanced for loop if you want to add or
remove elements while traversing an ArrayList. If an ArrayList is
modified, such as by calling the add or remove methods, while it is
being looped over, it will cause the loop to throw a
ConcurrentModificationException. If you need to modify an ArrayList
while looping over it, you’ll need to use a regular while or for loop.
What does the following code do? Guess before you run it. Then, add another enhanced for each loop that computes the product of all the elements in myList by multiplying them. Print out the product after the new loop.
7.3.2. For Loop¶
You can also use a while loop or a regular for loop to process list
elements accessed using an index. ArrayList indices starts at 0 just like
array indices, but instead of using the index operator [] to access
elements, you use the get(index) method to get the value at the index and
set(index,value) to set the element at an index to a new value.
If you try to use an index that is outside of the range of 0 to the number of
elements − 1 in an ArrayList, your code will throw an
IndexOutOfBoundsException, similar to the ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
thrown if you use the index operator on an array with an index out of bounds for
that array.
The following code will throw an IndexOutOfBoundsException. Can you fix
it?
7.3.3. While Loop¶
The example below demonstrates a while loop and an object-oriented approach
where the list is a field of the current object and you use an instance method
rather than a class (static) method to loop through the list.
The following code removes a name from a list. Set the found variable to the appropriate true or false values at line 13 and line 20 to make the code work.
Be careful when you remove items from a list as you loop through it. Notice how the method above only increments the index if an item was not removed from the list. This is because removing an item from a list will shift the remaining items to the left and if you increment the index in all cases you will skip the elements immediately after each element you remove. To see why, consider that those elements will be shifted into the position of the just removed element and if you increment the index, it will move to the next position, skipping the element that used to be at that position. Leaving the index unchanged after a remove allows the shifted-down element to be processed on the next time through the loop.
- [0, 4, 2, 5, 3]
- Incrementing the index each time through the loop will miss when there are two zeros in a row.
- [3, 5, 2, 4, 0, 0, 0, 0]
- This would be true if the code moved the zeros to the end, but that is not what it does.
- [0, 0, 0, 0, 4, 2, 5, 3]
- This would be true if the code moved the zeros to the font, but that is not what it does.
- [4, 2, 5, 3]
- This would be correct if k was only incremented when an item was not removed from the list.
7-3-4: Assume that nums has been created as an ArrayList object and it initially contains the following Integer values [0, 0, 4, 2, 5, 0, 3, 0]. What will nums contain as a result of executing numQuest?
ArrayList<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
private ArrayList<Integer> nums;
// precondition: nums.size() > 0;
// nums contains Integer objects
public void numQuest()
{
int k = 0;
Integer zero = new Integer(0);
while (k < nums.size())
{
if (nums.get(k).equals(zero))
nums.remove(k);
k++;
}
}
You can step through the code above by clicking on the following Example.
The following has the correct code for the method getScore plus at least one extra unneeded code statement. This method will calculate and return the score for a word game. The code should loop through all of the elements in wordList and if the length of the current word is 3 it should add one to the score, if the length of the word is 4 it should add 2 to the score, and if the length is greater than 4 it should add 3 to the score. The method should return the score. Drag the needed blocks from the left into the correct order on the right. Check your solution by clicking on the Check button. You will be told if any of the blocks are in the wrong order or if you need to remove one or more blocks. There is one extra block that is not needed in a correct solution.
The following has the correct code for a method called insertInOrder plus at least one extra unneeded code statement. This method should add the passed name in alphabetic order to a private list field called nameList. Drag the needed blocks from the left into the correct order on the right. Check your solution by clicking on the Check button. You will be told if any of the blocks are in the wrong order or if you need to remove one or more blocks. There is one extra block that is not needed in a correct solution.
7.3.4. ArrayList of Student Objects¶
You can put any kind of objects into an ArrayList. For example, here is an
ArrayList of Students. Although the print statement works here, you
may want a nicer printout.
Add a for each loop that prints out each student and then a new line.
7.3.5.  Programming Challenge : FRQ Word Pairs¶
Programming Challenge : FRQ Word Pairs¶
This challenge is based on the 2018 Free Response Question #2 WordPair. We encourage you to work in pairs on this challenge.
You are given a class called WordPair that can store pairs of words.
class WordPair
{
private String word1;
private String word2;
public WordPair(String word1, String word2)
{
this.word1 = word1;
this.word2 = word2;
}
public String getFirst()
{
return word1;
}
public String getSecond()
{
return word2;
}
public String toString()
{
return "(" + word1 + ", " + word2 + ")";
}
}
First, see if you can create an ArrayList of WordPair objects below.
Look at the StudentList example above for help.
Create an Arraylist of WordPair objects.
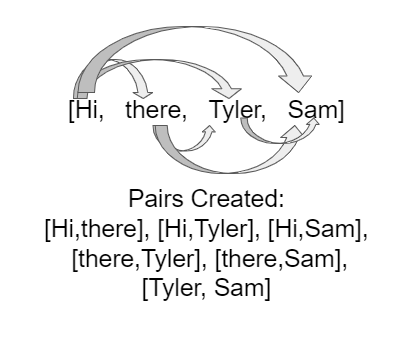
In this FRQ, you are given an array of words and you will create pairs of them by taking the first word and pairing it with all the other words, then taking the second word and pairing it with all but the first one, and so on. For example, if the word array is [“Hi”, “there”, “Tyler”, “Sam”], this figure shows how the word pairs are formed.
In the class WordPairsList below, you will write the constructor which takes
the array of words and pairs them up as shown in the figure. You will need
nested loops to pair each element with the rest of the elements in the list.
Here is the pseudocode for the constructor method.
Initialize the
allPairslist to an emptyArrayListofWordPairobjects.Loop through the
wordsarray for the first word in the word pair (for loop from indexi = 0tolength-1)Loop through the rest of the word array starting from index
i + 1for the second word in the word pair (for loop from indexj = i + 1tolength)Add the new
WordPairformed from theith word and thejth word to theallPairsArrayList.
FRQ WordPairs Challenge: Complete the constructor for WordPairsList below
which will add pairs of words from a given array to the ArrayList. Then,
complete the method numMatches() as described below this exercise.
In the next part of the FRQ challenge, you are asked to write a method called
numMatches that counts and returns the number of pairs where the first word
is the same as the second word. For example, if the word array is
["hi","bye","hi"], the pairs generated would be ["hi","bye"],
["hi","hi"], and ["bye","hi"]. In the second pair ["hi","hi"], the
first word is the same as the second word, so numMatches would return 1.
For this method, you will need a loop that goes through the ArrayList
allPairs and for each WordPair in allPairs, it checks to see if its
first word (using the getFirst method) equals the second word (using the
getSecond method). If there is a match, it increments a counter which it
returns at the end of the method. To test this method, add another “there” into
the words array and then uncomment the call to numMatches.
7.3.6. Summary¶
ArrayLists can be traversed with an enhancedforloop, awhileloop, or a regularforloop using an index.Deleting elements during a traversal of an
ArrayListrequires using special techniques to avoid skipping elements, sinceremovemoves all the elements above the removed index down.Since the indices for an
ArrayListstart at 0 and end at the number of elements − 1, accessing an index value outside of this range will result in anIndexOutOfBoundsExceptionbeing thrown.Changing the size of an
ArrayListwhile traversing it using an enhancedforloop can result in aConcurrentModificationExceptionbeing thrown. Therefore, when using an enhancedforloop to traverse anArrayList, you should notaddorremoveelements.


