15.7. SkyView - Part A¶
The following is a free response question from 2013. It was question 4 on the exam. You can see all the free response questions from past exams at https://apstudents.collegeboard.org/courses/ap-computer-science-a/free-response-questions-by-year.
Question 4. A telescope scans a rectangular area of the night sky and collects the data into a 1-dimensional array. Each data value scanned is a number representing the amount of light detected by the telescope. The telescope scans back and forth across the sky (alternating between left to right and right to left) in the pattern indicated below by the arrows. The back-and-forth ordering of the values received from the scan is called telescope order.
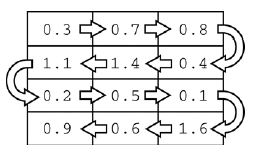
Figure 1: The first row is left to right and the second is right to left and so on.¶
The telescope records the data in telescope order into a 1-dimensional array of double values. This
1-dimensional array of information received from a single scan will be transferred into a 2-dimensional array,
which reconstructs the original view of the rectangular area of the sky. This 2-dimensional array is part of the
SkyView class, shown below. In this question you will write a constructor and a method for this class.
public class SkyView
{
/**
* A rectangular array that holds the data representing a rectangular area of
* the sky.
*/
private double[][] view;
/**
* Constructs a SkyView object from a 1-dimensional array of scan data.
*
* @param numRows the number of rows represented in the view Precondition:
* numRows > 0
* @param numCols the number of columns represented in the view Precondition:
* numCols > 0
* @param scanned the scan data received from the telescope, stored in
* telescope order Precondition: scanned.length == numRows * numCols
* Postcondition: view has been created as a rectangular 2-dimensional
* array with numRows rows and numCols columns and the values in scanned
* have been copied to view and are ordered as in the original rectangular
* area of sky.
*/
public SkyView(int numRows, int numCols, double[] scanned)
{
/* to be implemented in part (a) */
}
/**
* Returns the average of the values in a rectangular section of view.
*
* @param startRow the first row index of the section
* @param endRow the last row index of the section
* @param startCol the first column index of the section
* @param endCol the last column index of the section Precondition: 0 <=
* startRow <= endRow < view.length Precondition: 0 <= startCol <= endCol <
* view[0].length
* @return the average of the values in the specified section of view
*/
public double getAverage(int startRow, int endRow, int startCol, int endCol)
{
/* to be implemented in part (b) */
}
// There may be other instance variables, constructors, and methods
}
Part a. Write the constructor for the SkyView class. The constructor initializes the view instance variable to a
2-dimensional array with numRows rows and numCols columns. The information from scanned,
which is stored in the telescope order, is copied into view to reconstruct the sky view as originally seen
by the telescope. The information in scanned must be rearranged as it is stored into view so that the
sky view is oriented properly.
For example, suppose scanned contains values, as shown in the following array.

Figure 2: First example scanned array values¶
Using the scanned array above, a SkyView object created with
new SkyView(4, 3, values), would have view initialized with the following values.
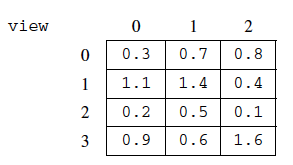
Figure 3: The resulting view from the first example scanned array¶
For another example, suppose scanned contains the following values.
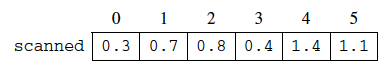
Figure 4: Second example scanned array values¶
A SkyView object created with new SkyView(3, 2, values), would have view initialized
with the following values.
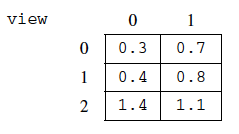
Figure 4: The resulting view from the second example scanned array¶
15.7.1. Try and Solve It¶
Complete the SkyView constructor in the class below.
The code below declares the class, the view, and a constructor for you to finish writing. It also has a main method for testing the constructor.
Complete the SkyView constructor in the class below.
