24.3. Set #2¶
The following questions make up Set #2 of the Practice Exam Questions. The questions resemble, both in format and substance, what you might see on the AP CS Principles exam. You should finish these questions within 17 minutes to satisfy the time constraints of the AP exam. You may refer to the AP CS Reference Sheet, which can be found here.
Click the “Start” button when you are ready to begin the exam. Click the “Pause” button to pause the exam (you will not be able to see the questions when the exam is paused). It will show how much time you have used, but you have unlimited time. Click on the “Finish Exam” button at the end when you are done. The number correct, number wrong, and number skipped will be displayed at the bottom of the page. Feedback for each answer will also be shown as well as your answer.
You will not be able to change your answers after you hit the “Finish Exam” button.
- Sending your address to a friend through a text message.
- Incorrect. This isn't phishing because there is no ill intent and there is no request made.
- Someone requesting your personal information through an online chat room.
- Correct. This is a clear example of phishing because it involves a request for information.
- Entering a website that attempts to infect computers with viruses.
- Incorrect. This is different from phishing because there is no request for information.
- Using someone’s software that searches for saved passwords on your computer.
- Incorrect. This is different from phishing because there is no request for information.
- I only
- Incorrect. The Internet does allow for quick spread of information, but it also can be accessed from different devices (phones, laptops, desktops, etc.)
- I, III only
- Correct. This is correct because The Internet is not made with security built-in, rather spread of informaton and availability are key goals.
- II, III only
- Incorrect. This is incorrect because the Internet is not made with security built-in.
- I, II, III
- Incorrect. This is incorrect because the Internet is not made with security built-in.
- Animal, Favorite Food
- Correct. The Name of the animal and an animal's Favorite Food do not influence total money made from selling the animals.
- Animal Size, Quantity, Favorite Food
- Incorrect. Quantity is important in calculating total money made because each animal costs a price and the total amount for an animal is (price x quantity).
- Animal, Quantity
- Incorrect. Quantity is important in calculating total money made because each animal costs a price and the total amount for an animal is (price x quantity).
- Favorite Food
- Incorrect. Favorite Food is not important for calculating price, but an Animal's name is not important for calculating total money.
- Animal Size, Quantity
- Incorrect. The quantity of animal isn't considered if trying to determine what food to prepare.
- Price, Quantity
- Incorrect. Price and quantity of an animal isnt considered when determining which food to prepare.
- Quantity, Favorite Food
- Incorrect. Favorite food is important for the manager to know, but quantity of animal is not important in determining what food to prepare.
- Animal Size, Favorite Food
- Correct. Animal size and favorite food are the two columns a manager would look at to determine which food to prepare.
- The run-time is directly proportional to the input size.
- Correct. This is true because every additional input requires the same amount of additional time.
- The run-time is inversely proportional to the input size.
- Incorrect. This is incorrect because the number of steps doesn't decrease with more inputs for this algorithm.
- The run-time of the program does not change with respect to the input size.
- Incorrect. The number of steps an algorithm goes through does influence the the time an algorithm takes to run for this algorithm.
- The run-time first increases and then decreases as the input size is increased.
- Incorrect. As the number of inputs increases, the number of steps in this algorithm will always be increasing in this case.
- Which of the following statements is true about the output of this circuit?
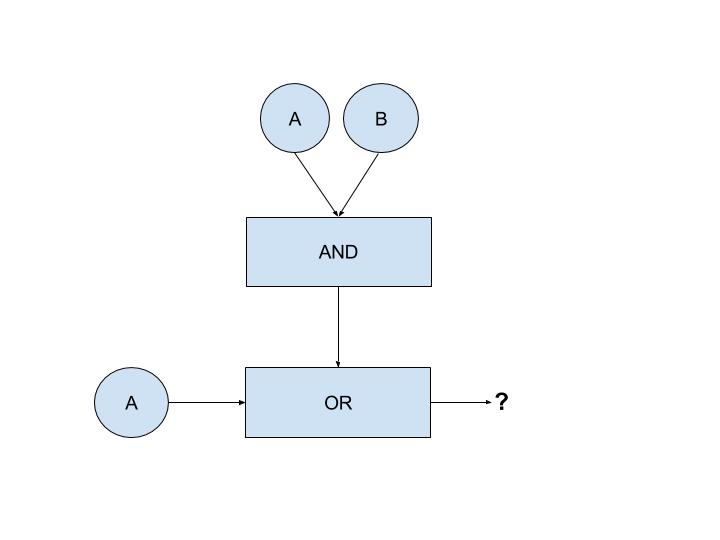
- The output of the circuit is always true
- Incorrect. If A is false, then the output is false in this circuit.
- The output of the circuit is the same as the value of input A
- Correct. If either A or B is false, then the second input to Or is false, thus the final output is dependent on the value of A.
- The output of the circuit is the same as the value of input B
- Incorrect. In all cases, the output depends on the value of A instead of the value of B
- The output of the circuit is always false
- Incorrect. If A is true, the circuit will always output true for a given B.
- I, II only
- Incorrect. These situations are correct, but there is another correct situtation.
- II, III only
- Incorrect. These situations are correct, but there is another correct situtation.
- I only
- Incorrect. This situation is correct, but there are more correct situations.
- I, II, III
- Correct. All three of these scenarios occur at the given n.
- Heuristic algorithm
- Correct. A Heuristic algorithm atempts to find an approximation of a solution without finding the exact solution.
- Brute-Force algorithm
- Incorrect. Brute-Forcing is trying to find a solution using trial and error.
- Recursive algorithm
- Incorrect. A Recursive algorithm is an algorithm that calls itself until a condition is met, at which point it stops.
- Dynamic Programming
- Incorrect. Dynamic Programming is breaking a problem into smaller sub-problems in order to find the correct answer.
- I. and II. only
- Incorrect. temp == 0 will cause the temperature to increment to 1 when temp == 0 and temp greater than 0 will cause the temperature to only increment above temp == 0.
- I. and III. only
- Incorrect. temp == 0 will cause the temperature to increment to 1 when temp == 0
- I. and IV. only
- Incorrect. temp == 0 will cause the temperature to increment to 1 when temp == 0
- III. and IV. only
- Correct. These two conditionals will not allow temp to go above 0
- A new electronic device that requires knowledge of the internal details, because it is important to know all the details of the device before using it.
- Correct. Abstraction doesn't require knowledge of internal details to understand the overall function of a device.
- A topographical map of the United States, because not all features of the geography are present, but the essence of the geography is present
- Incorrect. This is a good example because not every part of the real landscape is represented on a map, only key features.
- A painting by Picasso, because the painting does not contain as many details as a photograph, but it still communicates the emotion of the event being painted
- Incorrect. This is a good example because knowledge of details is not required to understand the overall concept.
- Pressing on the brake pedal of your car, because you don’t have to know how brakes work in order to stop the car
- Incorrect. This is a good example because knowledge of how a car brake functions is not required to press a car brake.
Which of the following is most likely to be a part of a phishing attack?
Which of the following statements is true regarding the benefits of using the internet?
I. The Internet allows information to be spread quickly from person to
person.
II. Internet users’ private information is protected regardless of
what they do on the Internet.
III. The Internet can be used from a variety of devices.
A pet store has a database of all of its animals with information about each animal. The database is shown below.
Animal |
Animal Size |
Price |
Quantity |
Favorite Food |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Rabbit |
Small |
$15.99 |
4 |
Carrots |
Dog |
Large |
$89.99 |
2 |
Dog Food |
Cat |
Medium |
$69.99 |
3 |
Catnip |
Fish |
Fish |
$9.99 |
8 |
Fish Pellets |
If the store manager wants to know how much money will be made by selling all the small animals, which of the following categories can be ignored when calculating this number?
A pet store has a database of all of its animals with information about each animal. The database is shown below.
Animal |
Animal Size |
Price |
Quantity |
Favorite Food |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Rabbit |
Small |
$15.99 |
4 |
Carrots |
Dog |
Large |
$89.99 |
2 |
Dog Food |
Cat |
Medium |
$69.99 |
3 |
Catnip |
Fish |
Fish |
$9.99 |
8 |
Fish Pellets |
If the store manager wants to prepare food for small size animals only, which of the following categories should he/she use?
If the number of steps that an algorithm takes is equal to a linear function of the input size, then which of the following statements is true regarding the runtime of the algorithm?
Consider the following code snippet that takes a positive integer ‘n’ as input and answer the question that follows
i <- 1
REPEAT UNTIL i ≤ n
IF i MOD 2 = 1
DISPLAY(“ODD”)
ELSE
DISPLAY(“EVEN”)
i <- i + 1
Which of the following statements are true?
I. “ODD” is printed n/2 times if n is even
II. “ODD” is printed (n + 1)/2 times if n is odd
III. “EVEN” is printed (n - 1)/2 times if n is odd
The Traveling Salesman Problem is a problem in theoretical computer science in which one tries to find the shortest route that passes through every point in a set, once and only once. The optimal solution to the problem for an arbitrary set of of points cannot be found in a reasonable amount of time, that is, it cannot be found in polynomial time. However, we can find an approximation to the optimal solution in a reasonable amount of time. It would be best to find the approximate solution using a
In a freezer, the temperature can be increased, but should not go above 0° C. It can, however, be exactly equal to 0° C. The unfinished code for increasing the temperature in a freezer is shown below. The variable temp represents the current temperature in degrees Celsius.
PROCEDURE incrementTemperature(temp)
{
IF (<MISSING CODE>)
{
temp ← temp + 1
}
RETURN temp
}
Which of the following conditional statements will allow the code to function as expected?
I. temp == 0
II. temp > 0
III. temp < 0
IV. NOT (temp >= 0)
What is NOT a good example of abstraction?