Section 7.1 Use Math
Subgoals for using libraries:.
-
Import module or function (if needed)
- With alias (optional)
-
Determine whether parameters are appropriate for function
- Number of parameters passed must match function documentation
- Type of parameters passes must match function documentation
- Determine what the function will return (i.e., data type), print, and/or change state of arguments and where it will be stored (nowhere, somewhere)
- Evaluate expression as necessary
Subsection 7.1.1
Problem:
Given the following code:
a_number = int(input("What number do you want to know the length of?"))
Use the
log10 function of the built-in math library to calculate the number of digits in a number taken from the user.Subsection 7.1.2 1. Import module or function (if needed)
First, we need to import the desired library, which is named
math. We do not need to alias the name because math is already short and descriptive.import math
Subsection 7.1.3 2. Determine whether parameters are appropriate for function
According to the documentation, the
log10 function consumes x, which is an integer.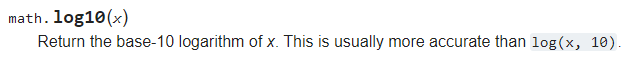
That integer is the value we will get from the user.
math.log10(a_number)
Subsection 7.1.4 3. Determine what the function will return (i.e., data type), print, and/or change state of arguments and where it will be stored (nowhere, somewhere)
The function will return the base-10 logarithm of X, which will tell us the number of digits required. Since we need to print the result, we’ll need to store the function call’s result in a variable
digits.digits = math.log10(a_number)
Subsection 7.1.5 4. Evaluate expression as necessary
We then finish the program by printing:
print(digits)
Answer.
The completed program:
import math
a_number = int(input("What number do you want to know the length of?"))
digits = math.log10(a_number)
print(digits)
You have attempted of activities on this page.
